Your cart is currently empty.
Cart

Manifesto Architecture
The Ghost of Mies
Edited by Nikolaus Hirsch, Markus Miessen
Featuring artwork by Dan Graham
The history of the avant-garde (in art, architecture, literature) can’t be separated from the history of its engagement with mass media. It is not just that the avant-garde used media to publicize its work; the work did not exist before its publication.
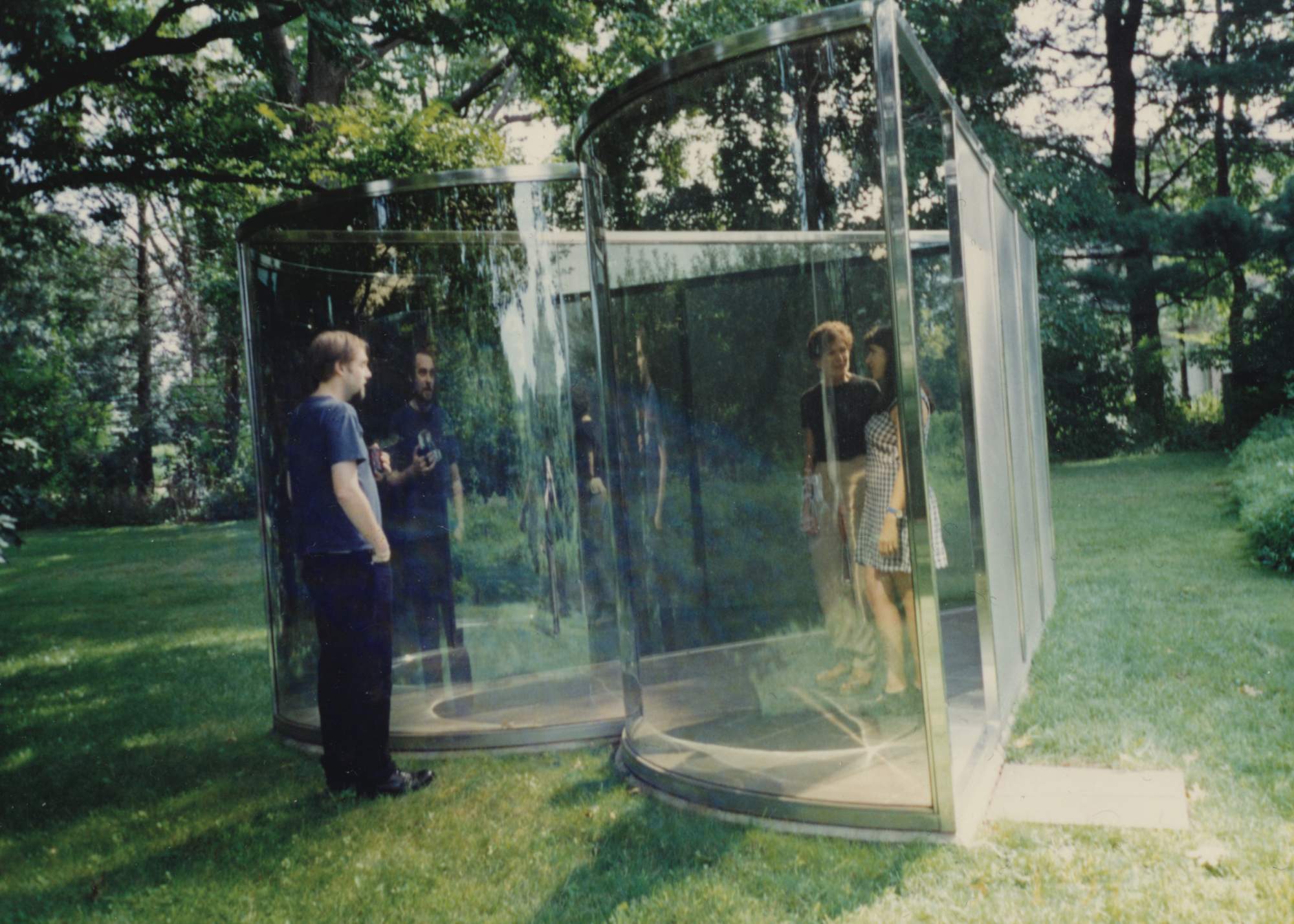
In architecture, Adolf Loos, Le Corbusier, and Mies van der Rohe came to be known through their influential writings and manifestos published in newspapers, journals, and little magazines. Entire groups, from Dada and Surrealism to De Stijl, became an effect of their manifestos. The manifesto was the site of self invention, innovation, and debate. Even buildings themselves could be manifestos. The most extreme and radical designs in the history of modern architecture were realized as pavilions in temporary exhibition.
In the third book in the Critical Spatial Practice series, Beatriz Colomina traces the history of the modern architecture manifesto, with particular focus on Mies van der Rohe, and the play between the written and built work. This essay propels the manifesto form into the future, into an age where electronic media are the primary sites of debate, suggesting that new forms of manifesto are surely emerging along with new kinds of authorship, statement, exhibition, and debate.